Many finance experts and business owners take modern accounting practices for granted. And why wouldn’t they — contemporary accounting professionals can record and analyze financial transactions in just a few clicks.
But have you ever wondered how this profession evolved over centuries, starting from the humble beginnings of clay tablets? The history of accounting is a fascinating journey that spans millennia, witnessing remarkable innovations and technological advancements.
In this post, we’ll explain the evolution of the accounting profession — from primitive accounting methods to modern accounting services, and everything in between.
Ancient accounting methods
The roots of accounting can be traced back to the cradle of civilization itself. One of the earliest known examples of accounting comes from the ancient Mesopotamian civilization, which flourished in the region that is now modern-day Iraq around 4,000 BCE.
The Mesopotamians used clay tablets to record transactions, creating a system that would lay the foundation for future accounting practices. In Mesopotamia, merchants engaged in extensive trade networks, and they needed a way to keep track of their goods and transactions.
These early accountants used simple notations on clay tablets to record the movement of goods: livestock, grain, and other commodities. Each clay tablet represented a record of a specific transaction or an inventory of goods.

However, accounting in ancient times wasn’t limited to tracking tangible assets alone. In the ancient Egyptian civilization, which thrived around 3,000 BCE, administrators used a system of record-keeping known as "hieratic script" to keep track of the kingdom's resources.
These early scribes meticulously documented the production and distribution of goods, such as food, clothing, and tools, in order to maintain order and ensure accountability.
Ancient accounting systems seem rudimentary compared to today's sophisticated software and auditing systems, but they laid the groundwork for the principles that still underpin modern accounting practices.
Double-entry bookkeeping and Renaissance innovations

Accounting historians didn’t record any major breakthroughs in the profession before the Renaissance, but this period turned out to be a game changer.
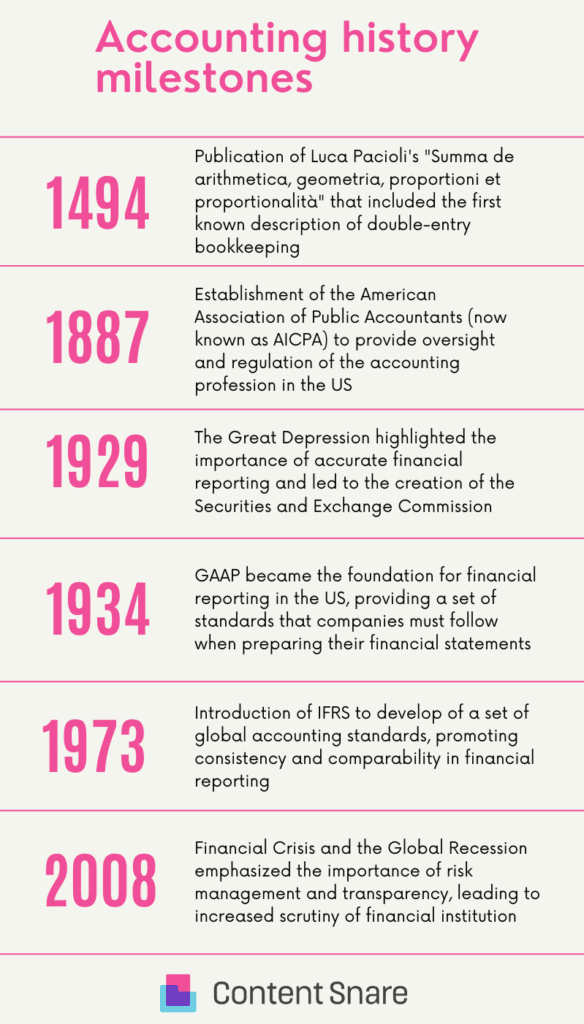
Double-entry bookkeeping, a fundamental concept in modern accounting, emerged in the late 15th century. One of the key figures in this development was Luca Pacioli, often referred to as the "father of accounting."
| Luca Pacioli: The father of accountingLuca Pacioli, an Italian mathematician and Franciscan friar, is credited with formalizing the system of double-entry bookkeeping in his seminal work, "Summa de Arithmetica, Geometria, Proportioni et Proportionalita," published in 1494. Pacioli's work served as a comprehensive guide to mathematics and included a section on accounting, which introduced the concept of double-entry bookkeeping. |
Double-entry bookkeeping revolutionized the accounting profession with a more methodical approach to recording financial transactions.
The system is based on the principle that every transaction has two aspects: a debit and a credit. For every debit entry, there must be an equal and opposite credit entry, ensuring that the books always balance.
The double-entry system offered several advantages over the previous single-entry models. By recording both the inflows and outflows of resources, double-entry bookkeeping led to:
- More accurate representation of a company's or merchant’s financial position
- Better tracking of revenues and expenses
- Faster error or discrepancy detection
Pacioli's work on double-entry bookkeeping laid the foundation for the development of modern accounting practices. During the Renaissance, the dissemination of knowledge and the invention of the printing press facilitated the spread of his ideas across Europe.
Industrial revolution and the rise of modern accounting

The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century, brought about significant changes to society, economy, technology, and accounting. As industries expanded and global trade flourished, the need for technically proficient accountants capable of sophisticated calculations became apparent.
They embraced emerging technologies like the telegraph to facilitate communication and the exchange of financial information over long distances. This allowed companies to expand their operations across regions and even continents, creating a need for standardized accounting practices.
The expansion of industrial activities also created a demand for specialized accounting professionals. They got many new roles in the following areas:
- Financial management
- Cost analysis
- Decision-making processes
- Taxation and trading activities
In such circumstances, it was important to create professional accounting bodies and associations. Here are some of the first (and most notable):
- Deloitte, one of the Big Four accounting firms, was founded in 1845 in London
- The Edinburgh Society of Accountants (1853)
- Institute of Chartered Accountants of Scotland (1854)
- Institute of Chartered Accountants in England and Wales (1880)
- CPA Australia (1886)
- The American Association of Public Accountants (1887)
- The American Society of Certified Public Accountants (1921)
Technological advancements in the 20th century

The 20th century was a period of unprecedented technological innovations that revolutionized accounting. The most significant advancement was the widespread adoption of electronic calculators and computers.
Electronic calculators were designed in the 1960s, and they drastically reduced the need for manual calculations. This made arithmetic tasks faster and much more accurate, helping accountants to perform complex operations with ease.
However, the introduction of computers in the late 1980s and their subsequent miniaturization set the stage for the modern profession. With the ability to store and process large amounts of data, computers enabled the development of sophisticated accounting software. These systems automated many routine accounting tasks:
- Journal entries
- Ledger maintenance
- Financial statements
- Audit reports
Accountants could rely on computers to handle repetitive tasks while they were focusing on analysis and interpretation. But that wasn’t the only impact computers made on accounting systems. Paired with the Internet, they also created preconditions for real-time accounting.
Real-time accounting enabled businesses to capture and process financial data instantaneously, providing up-to-date information for decision-making. This was particularly beneficial for multinational corporations with operations spread across different locations and time zones.
Contemporary accounting

In the contemporary accounting landscape, technology continues to shape the profession. Accounting systems now use a range of tools and technologies, but one of them dominates the business — cloud computing.
Cloud-based accounting software enables business professionals to store and access financial data securely on remote servers. This eliminates the need for physical storage and enables real-time collaboration between accountants and clients.
Accounting evolution: What’s next?
The history of accounting has always been a story of innovation. Looking ahead, the future of the profession is destined to follow the same pattern by embracing technologies like blockchain and AI. Accounting firms will need to adapt to these evolving landscapes and develop expertise in managing and safeguarding digital assets.

