Here’s an interesting fact: WordPress turns 20 this year.
This content management system (CMS) is fairly old from an IT perspective, but it has aged well. Today, WordPress is by far the most popular CMS platform, powering nearly 45% of all websites on the Internet.
But how did it get there?
Well, we have to dig deep into the history of WordPress to understand how it became such a mammoth CMS. In this article, we’ll dive deep into WordPress history and the entire ecosystem surrounding this incredible platform.

History of WordPress: A brief overview
WordPress is an open-source CMS for creating all sorts of websites. Its co-founders, Matt Mullenweg and Mike Little, launched the platform on May 27, 2003.
Their idea was to simplify blogging. Mullenweg and Little designed WordPress as an easy-to-use blogging system suitable even for authors with no technical knowledge. The initial version of WordPress was based on an existing blogging platform b2/cafelog, which was no longer being actively developed.
Slowly but surely, WordPress evolved by adding different functionalities. The platform drastically changed in 2004 because it enabled users to add plugins and themes. This was a big breakthrough—it allowed admins to tailor the look and functionality of their websites.
New features helped WordPress become the most popular CMS on the web by 2011. The system has been improving ever since, attracting more users every year. Fast forward to 2023 and 835 million websites are powered by WordPress.
And that’s just one of the fascinating WordPress stats you should know in 2023.
WordPress.com vs. WordPress.org
One of the rare details that still confuse people is the existence of two different platforms: WordPress.com and WordPress.org. Though the two systems use the same software, they are not the same thing.
WordPress.com is a hosted platform.
That means the company running the system does most of the work for you. With WordPress.com, you don't need to worry about web hosting, security, backups, or updates. In other words, it’s easy to create a website without any technical knowledge or experience. The company behind WordPress.com is Matt Mullenweg’s Automattic.
WordPress.org, on the other hand, is a self-hosted platform.
That means you can download and install the WordPress software on your own web hosting server. It requires some technical knowledge and experience to set up, but gives you complete control over your website. You are free to customize the design, add features with plugins, and monetize your site with ads.
Notable WordPress versions

WordPress’s history is packed with new releases, so it’s pointless to discuss each version separately. We will, however, focus on major versions of the system in order to explain how this CMS has changed over the years and decades.
WordPress 1.0 (2004)
One of the first versions of WordPress brought many changes to older CMS formats. First of all, it included search-engine-friendly permalinks that Google and other systems could recognize easily. WordPress 1.0 also introduced comment moderation, page editing, and additional template tags.
WordPress 2.0 (2005)
WYSIWYG (what you see is what you get) editing is the most important improvement in WordPress 2.0. The feature took blogging to a higher level by helping authors edit content in a single WordPress dashboard. But there were other notable additions, including these:
- Spam and backup plugins like Aksimet and Skippy’s DB
- Post preview and faster posting
- Theme functions
WordPress 3.0 (2010)
The 3.0 version of WordPress was launched in 2010. What makes this one different is the introduction of the then new theme called Twenty Ten. WordPress 3.0 had a lighter interface compared to its predecessors, as well as bulk plugin updates and contextual help on each screen. This version also proved the power of the WordPress community—more than 200 contributors worked together on this project.
WordPress 4.0 (2014)
WordPress 4.0 didn’t introduce revolutionary upgrades, but it did add extra functionalities to make the user experience smoother. Content creators could count on better media management thanks to the brand new grid with easy previews. The 4.0 editor was able to adjust to fit content, while the plugin directory was improved to simplify search.
WordPress 5.0 (2018)
WordPress launched its famous block-based editor, aka Gutenberg, in 2018. With this feature, each piece of content got its own block that users could rearrange without changing anything else. It was a groundbreaking solution that marked the recent history of WordPress. Gutenberg remains the default editor even in 2023.
WordPress 6.0 (2022)
One of the latest versions of the platform mainly focused on the writing experience. It added a range of features to simplify content creation. That includes style switching, additional sizing controls, and new design tools.
These are just a few of the major updates that WordPress has undergone over the years. Each release has helped to make the platform more powerful and flexible. At the moment, WordPress 6.2 is in the testing phase.
A brief history of WordPress plugins
Plugins have been an integral part of the WordPress ecosystem since the very beginning. At the time, WordPress was primarily a blogging platform with limited functionality. But as it grew in popularity, developers started creating plugins to extend its functionality.
The first official plugin repository was launched in 2005. By the end of the year, 100 plugins were available for download. These tools were mostly designed by independent WordPress developers. They were simple in nature, providing basic functionalities like adding a contact form or images to a web page.
Akismet was one of the first truly important WordPress plugins. Automattic’s anti-spam tool quickly became essential for the performance of WordPress sites, and it was eventually bundled with the CMS in version 2.0.
Today, you can find over 60 thousand items in the WordPress plugin directory, as well as countless premium plugins.
One of the reasons for such a huge number of WordPress plugins is that they are relatively easy to create. Developers can make plugins using many programming languages, including PHP, JavaScript, and CSS. They can also use third-party frameworks and libraries, such as jQuery and Bootstrap, to speed up development time.
A brief history of WordPress themes
You can now find over 10 thousand items in the WordPress theme directory, but how did it look in the beginning?
It all started with the Classic theme, which wasn’t even a true theme from today’s perspective. This one focused on the blogging essentials, leaving most of the space for textual content. The Classic theme looks outdated now, but it used to be a big deal among WordPress users back in 2004.
What is a WordPress theme?
A WordPress theme is a pre-designed template that determines the layout, design, and functionality of a website. In a nutshell, it’s a collection of files that work together to create the visual appearance and functionality of the site. Themes consist of three components:
- Stylesheet
- Template
- PHP files
These elements determine how the content is displayed on the WordPress site.
The second major theme — and the first one with modern functionalities — is Default/Kubrick. It was released in 2005, and it instantly impressed admins with its intuitive user interface and simple navigation.
After Kubrick, WordPress started releasing a new default theme with each CMS update. From 2010 to 2023, a new default theme has been published every year.
In the modern age of websites, WordPress themes have become more important than ever. It’s impossible to build a highly functional website without mobile-friendly themes. They also contribute to the overall speed, performance, and usability of WordPress sites.
That’s why users can now choose from a range of options — from simple and minimalist designs to complex and feature-rich themes.
WordPress community and ecosystem
As an open-source platform, WordPress attracts millions of users and contributors from all over the world. The WordPress community is a network of developers, designers, bloggers, and CMS enthusiasts.
The key strength of the WordPress platform is its open-source nature. Anyone can contribute to the development of the system by:
- Submitting patches
- Suggesting new features
- Helping with documentation
This open approach made it possible to improve the platform and build a massive ecosystem of plugins and themes.
WordPress also has an active online community. You can find countless forums, blogs, and social media groups dedicated to discussing and sharing information about the platform. You can find it all—support, advice, and insights on using WordPress. Some of the main community contributors include:
- Developers: This community is home to thousands of developers who contribute to the WordPress core software. They often collaborate on projects and share their knowledge with one another, creating a thriving community of experts.
- Designers: A large community of designers creates custom themes, templates, and user interfaces for WordPress websites.
- Consultants: WordPress consultants provide advice and guidance to clients who want to use WordPress for their website or business. They help with website planning, content strategy, or technical issues.
- Hosting providers: Many providers offer WordPress-specific hosting plans.
- E-commerce providers: WordPress also has a thriving e-commerce ecosystem, with numerous plugins and themes available to help businesses build and run their online stores. These providers often specialize in specific e-commerce platforms, such as WooCommerce or Easy Digital Downloads.
Bloggers, marketers, influencers, educators, and many other stakeholders also contribute to the ecosystem. Together, they create a versatile community that supports and drives the growth of the platform.
WordCamp: A place to discuss all things WordPress
The WordPress community is not exclusively virtual. WordPress developers and other CMS professionals gather at WordCamps. These are casual, locally-organized conferences covering everything related to WordPress.
It’s a place where members of the WordPress community can share ideas, collaborate, and learn from each other. The first WordCamp took place in San Francisco in 2006, attracting over 500 participants. Matt Mullenweg organized the event with help from a group of volunteers.
The first WordCamp featured talks from some of the most influential members of the WordPress community, including Matt Mullenweg and Ryan Boren, former lead developer at WordPress.
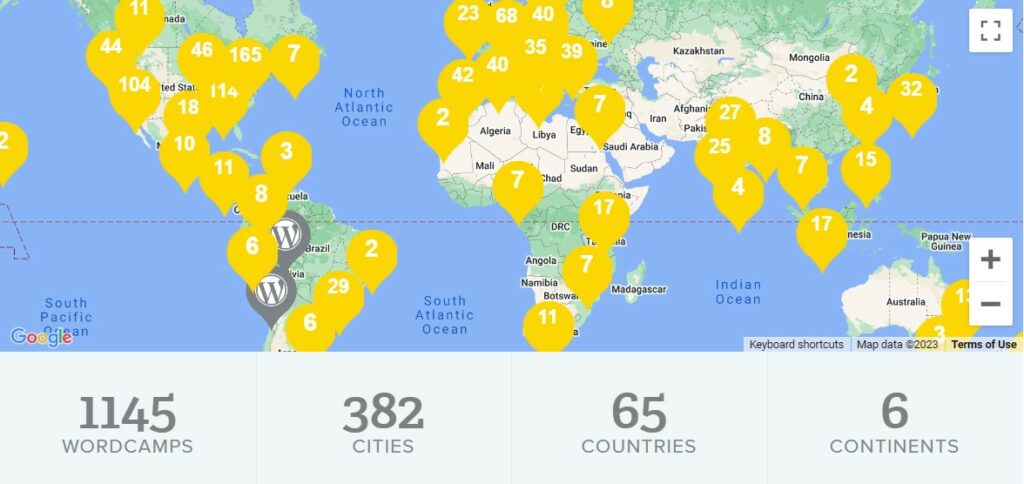
The success of the first event inspired the community to organize new gatherings, both in the United States and abroad. The first international WordCamp was held in Beijing, in September 2007. Over the years, WordCamp has continued to grow in popularity and scope. In addition to talks and workshops, they also feature discussions, networking events, and social gatherings.
To date, there have been over 1,100 WordCamps in 65 countries.
WordPress history: A sign of a bright future
WordPress has come a long way from its humble beginnings as a blogging platform. It has been growing steadily since 2003, becoming better, more powerful, and more versatile. But what does the future hold for this CMS?
One thing's for certain: WordPress isn't going anywhere anytime soon. It’s more relevant than ever before, so we can only expect it to keep evolving and adapting to the changing needs of its users. However, we don’t expect it to abandon its core principles of simplicity, flexibility, and openness.