Picture this: You mention the word "bookkeeping" in a conversation, and suddenly everyone's eyes glaze over, stifling a yawn. We’ve seen it happening too many times, as most people believe bookkeeping is just plain boring.
What they don't know is that the history of bookkeeping is anything but dull. Behind those seemingly mundane numbers lies a world of improvisation and creative thinking. In this post, we’ll walk you through the millennia of bookkeeping history.
Related: Accounting history: From clay tablets to cloud computing
Early origins of bookkeeping

We can trace the early origins of bookkeeping all the way back to ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia and Egypt. Here’s how they influenced the development of primitive accounting methods.
The birth of writing in Mesopotamia
One of the earliest known civilizations to develop a writing system was ancient Mesopotamia, situated in the fertile valleys between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers (modern Iraq).
Mesopotamians faced the challenge of managing the surplus of agricultural production and trade, so they needed a reliable way to document trade and production reports. Around 3500 BCE, they invented cuneiform script, a system of wedge-shaped marks made on clay tablets.
This allowed those early accountants to keep a detailed record of barter transactions and other trade-related information. These clay tablets became the precursors to modern-day ledgers.
Papyrus took the game to another level in ancient Egypt
Not too far away from Mesopotamia, the ancient Egyptian civilization developed papyrus as a writing material. They used papyrus scrolls as the medium for bookkeeping records and financial transactions.
The Egyptians maintained meticulous records of economic transactions, taxation, and the distribution of resources:
- Detailed accounts of the harvest
- The allocation of labor
- The distribution of goods and services
In a way, these were the first (though primitive) traces of financial accounting as we know it today. These records and accounting systems helped the Egyptian civilization maintain a huge centralized economic system.
Roman bookkeeping and the advent of commercial accounting

The Romans recognized the vital role of bookkeeping in facilitating trade and establishing trust among merchants. One of the reasons for the adoption of bookkeeping practices in ancient Rome was the widespread use of coins as a medium of exchange.
The introduction of standardized coinage, such as the denarius, enabled merchants to conduct business more efficiently. However, it also required a reliable method of tracking transactions, giving the extra push to primitive accounting methods. In addition, bookkeeping played a vital role in the administration of the entire Roman Empire.
The state, with its extensive bureaucracy and complex tax system, relied on accurate accounting to collect revenue. The Roman government appointed quaestors, officials responsible for financial statements, who oversaw the meticulous bookkeeping and auditing of public accounts. This laid the foundation for independent financial reviews.
Related: How much to charge for bookkeeping
Italian Renaissance: The birth of double-entry bookkeeping
Bookkeeping practices remained the same for centuries, but a really big change took place during the Renaissance period. We are talking about double-entry bookkeeping, a truly revolutionary method of recording financial processes.
Luca Pacioli, a Franciscan friar and mathematician, was the person who made it possible. In 1494, Pacioli published "Summa de Arithmetica," a comprehensive treatise on mathematics and its practical applications. This work became one of the most influential books of its time, but its lasting impact on the world of business transactions and finance is what truly distinguishes it.
One of the chapters in this book is titled "Particularis de Computis et Scripturis" (Details of Calculation and Recording). It was in this chapter that Pacioli described the concept of the double-entry bookkeeping system for the first time.
Although the double-entry system had been in practice prior to his publication, Pacioli's work brought it to the forefront and solidified its importance as a standard practice. The double-entry bookkeeping system set the stage for modern professional accounting and remained a cornerstone of financial management to this day.
Evolution of Bookkeeping in the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution spanned from the late 18th to the early 19th century, and it brought about a new shift in economic and technological advancements. This era marked a transition from manual labor to machine-based manufacturing processes.
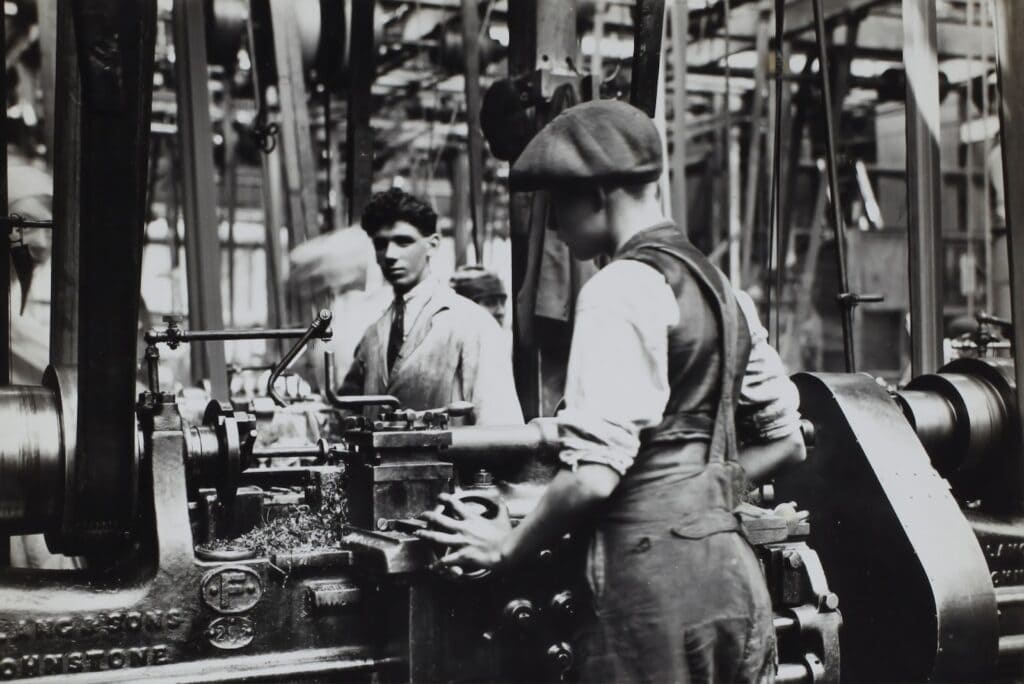

It gave birth to large-scale enterprises and complex financial transactions, so bookkeeping practices had to adjust. Enterprises in this era began to adopt specialized journals and ledgers that streamlined the record-keeping process. These transactions included the information needed for crafting financial statements, such as:
- Sales data
- Purchases
- Cash receipts
- Cash disbursements
Businesses used to record each transaction as it occurred, so they could gain a clearer picture of their financial activities. At the same time, ledgers provided a centralized repository for posting and summarizing accounting records.
They categorized detailed financial information according to specific accounts (accounts receivable, accounts payable, inventory, capital, etc.), helping companies track individual accounts and generate financial statements. All those little innovations allowed for greater accuracy in record-keeping, reducing the risk of miscalculations and discrepancies.
Modern bookkeeping practices
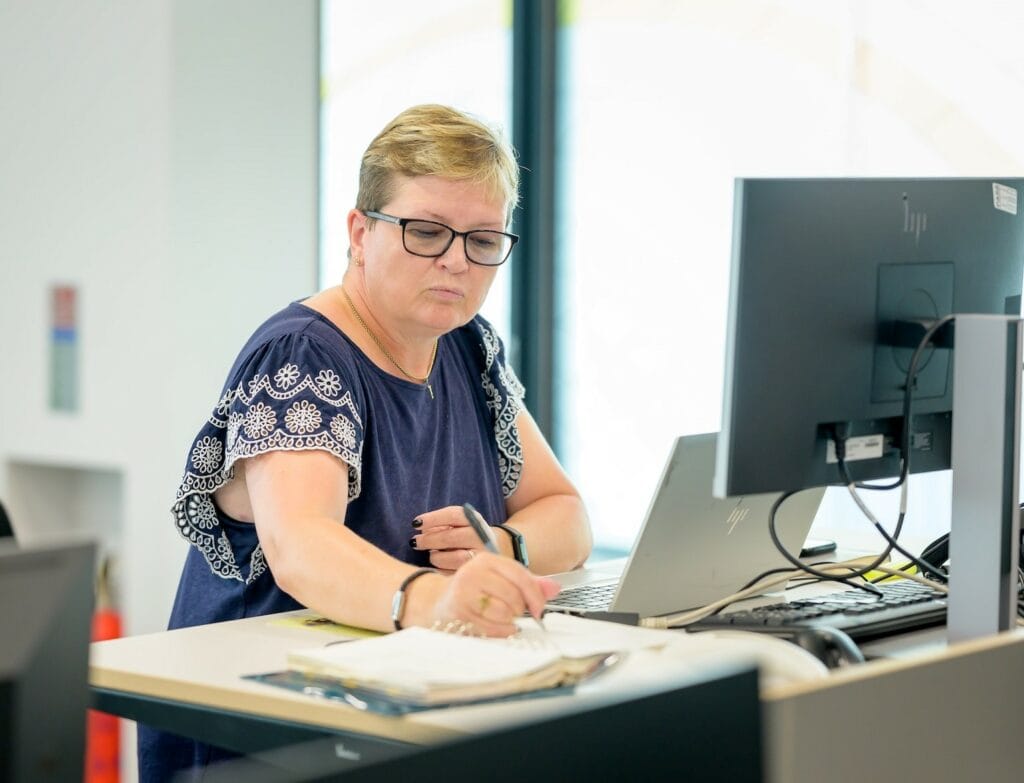

In the 20th century, bookkeeping was primarily a manual and paper-based process. This system was time-consuming and prone to human errors, making it difficult to keep up with the increasing complexity of financial records.
But calculators and computers changed the game in the second half of the 20th century. Specialized bookkeeping software was particularly important because it streamlined data management for bookkeeping purposes.
Bookkeepers could now enter data into electronic spreadsheets and perform calculations automatically. This shift allowed businesses to handle a huge collection of financial data and generate more detailed financial reports.
Related: Workflow software for accountants — our top 9 picks
Cloud-based systems of the 21st century
The digital revolution accelerated as we entered the 21st century, bringing forth cloud-based bookkeeping tools. This type of bookkeeping enables data management through remote online servers. The benefits of cloud-based systems are paramount:
- Business owners and bookkeepers can access financial data from anywhere at any time
- The system enables real-time collaboration
- Cloud-based bookkeeping offers enhanced data security and disaster recovery measures
- These platforms integrate with other business applications and financial tools
Recording financial transactions: What’s next?
Bookkeeping has come a long way from its humble beginnings in ancient civilizations, but the future seems to hold even more exciting possibilities. It’s hard to predict what will come next, but we believe that AI and machine learning will lead to further automation, while cloud-based systems will become the norm.
Digital solutions will keep replacing manual processes, making the entire bookkeeping profession more efficient and accurate.